Understanding the Single-Threaded Nature of Node.js
Introduction: Node.js, a powerful and widely-used runtime for server-side JavaScript, is well-known for its non-blocking, event-driven architecture. One of the key features that sets Node.js apart from other server-side technologies is its single-threaded nature. In this article, we will explore the reasons behind Node.js being single-threaded, how it manages concurrency, and the advantages and challenges associated with this design choice.
1. Single-Threaded Architecture:
At its core, Node.js operates on a single-threaded event loop. Unlike traditional multi-threaded approaches used by many server-side technologies, Node.js relies on a single execution thread to handle all incoming requests. This design decision is rooted in the asynchronous, non-blocking nature of JavaScript.
2. JavaScript and Event-Driven Programming:
Node.js leverages the JavaScript language, which is inherently single-threaded. JavaScript was initially designed to run in web browsers, where responsiveness is crucial for providing a smooth user experience. This single-threaded nature carries over to Node.js, where it is employed to handle server-side tasks efficiently.
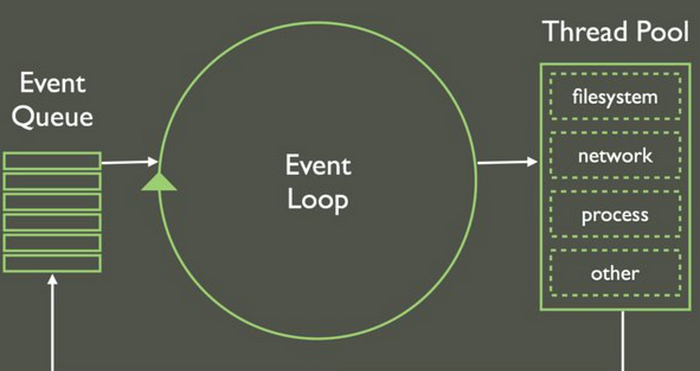
3. Event Loop:
The event loop is a fundamental concept in Node.js that enables it to efficiently manage concurrent operations. The event loop continuously listens for events, such as incoming requests or completed I/O operations, and executes the associated callback functions. This approach allows Node.js to perform non-blocking I/O operations, ensuring that the server remains responsive even under heavy loads.
4. Non-Blocking I/O:
Node.js employs non-blocking I/O operations to handle multiple requests simultaneously. When an asynchronous operation is initiated, such as reading from a file or making a network request, the event loop is free to process other tasks while waiting for the operation to complete. This non-blocking nature is crucial for scalability, as it allows Node.js to handle a large number of concurrent connections without creating a thread for each one.
5. Advantages of Single-Threaded Model:
a. Scalability: Node.js can handle a large number of concurrent connections due to its non-blocking nature.
b. Simplicity: The single-threaded model simplifies the development process by eliminating the need for complex synchronization mechanisms used in multi-threaded environments.
c. Efficiency: Node.js can efficiently manage I/O-bound tasks, making it well-suited for applications with a high level of concurrent I/O operations.
6. Challenges and Mitigations:
a. CPU-bound Tasks: Node.js may face challenges with CPU-bound tasks, as its single-threaded nature means it cannot fully utilize multi-core processors. Clustering and the use of worker threads can help mitigate this limitation.
b. Blocking Operations: Developers need to be cautious with synchronous, blocking operations, as they can impact the responsiveness of the event loop. Asynchronous alternatives should be preferred.
Conclusion: Node.js’ single-threaded architecture, built on the principles of non-blocking I/O and event-driven programming, has proven to be a powerful and scalable solution for building high-performance server-side applications. While it has its challenges, the advantages of simplicity, efficiency, and scalability make Node.js a popular choice for a wide range of applications in the modern web development landscape. Understanding the event loop and asynchronous programming is essential for harnessing the full potential of Node.js.
